One of the most common questions we get has to do with white-spaces and element widths, which are usually caused by the CSS margin or padding property on an element (an HTML component) of a webpage. Solving this involves two parts:
- Find the element causing the issue, and then identify the CSS property using inspect element
- Make a customization/change to the class to fix the issue in Admin -> Appearance -> Customize -> Additional CSS
Inspect Element is a necessary tool for anyone running a website or blog.
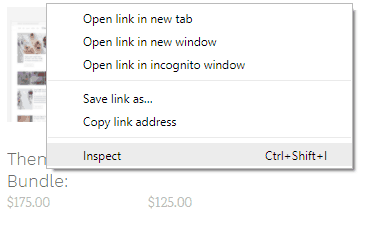
Everyone can access it by right clicking on the element you want to inspect, and clicking on "Inspect" in Chrome and Safari, or "Inspect Element" in Firefox. No plugins are needed.
It's important to be aware that what you see when you're logged in as an Admin, and what users who aren't logged in see, are often different. We recommend using Chrome or Firefox (or Safari on Mac) to do your admin management, and another browser to view your website like a user that isn't logged in.
Right clicking on an element and using "Inspect Element" gives you a list of CSS properties and computed layout options. In most modern web browsers, you can even edit the CSS in the "inspect element" to see live changes to your site, but these changes are not saved and are lost when you leave the page or refresh. It's a great way to troubleshoot.
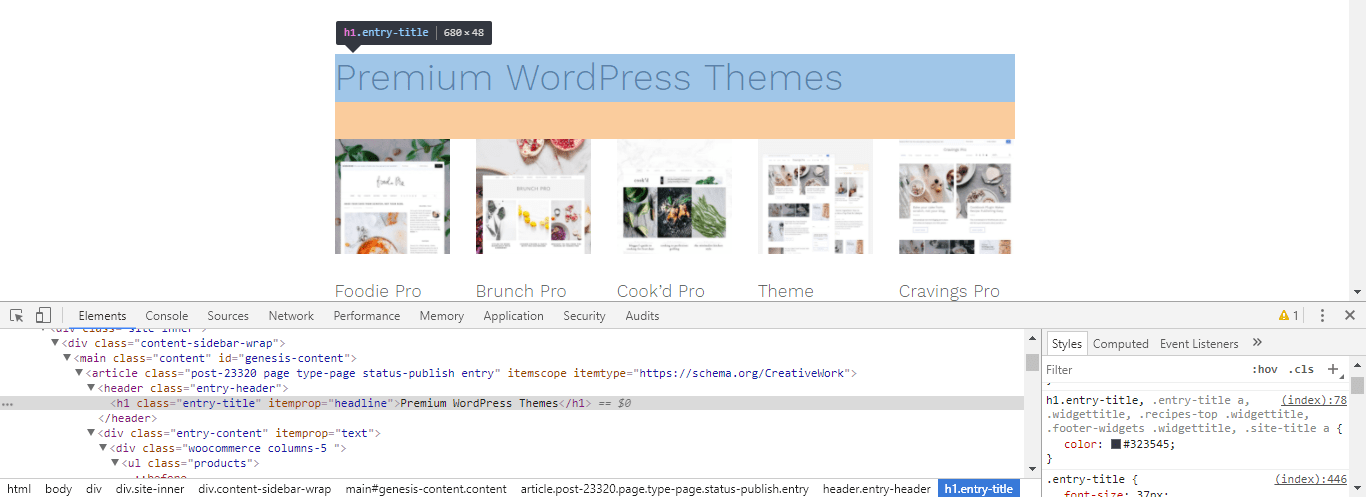
Inspect Element Components
Here's a breakdown of what you see in the "inspect element" feature.
- The highlighted blue portion shows the element that's being inspected, with the highest level attribute (h1.entry-title)
- The orange below visually displays this element's margin-bottom property, and in this case indicates there are no side or top margins and no padding properties by the lack of being displayed.
- In the new "Elements" window that appears at the bottom (or side sometimes, depending on your browser setup) you have a modified view-source that removes some source code, while formatting (indents and color coordination) the more relevant parts
- At the very bottom you'll see a consecutive list of elements that are "parent" elements going from left to right, of the element you're inspecting. Each of these has a possibility of passing on properties to the inspected element through "inheritance", where properties such as background-color and font-style are passed along to nested elements.
- In the bottom-right you'll find the "Styles" and "Computed" tabs, which show you the final properties of the element you're currently inspecting. Here we see that the h1.entry-title is being given the "color: #323545;" property by (index), which is CSS embedded in this page.
With this information, if we wanted to change the font color for the h1.entry-title element, we can go into our Admin -> Appearances -> Customize -> Additional CSS page and add our own entry like:
h1.entry-title { color: red; }
Or any hex color value in place of "red".
For further reading, see: https://developers.google.com/web/tools/chrome-devtools/inspect-styles/
Learning CSS
Not familiar with CSS? It's fairly basic and can do almost everything you need to from a design perspective. Learning how it works is like seeing into the Matrix for the first time. Things you never knew were there suddenly become apparent, and the ability to change the web is powerful. We recommend checking out the following:
- https://www.freecodecamp.org/challenges/say-hello-to-html-elements
- https://web.dev/learn/css
- https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-css
- https://www.w3schools.com/css/
FreeCodeCamp is a personal favourite of ours. It gives you short, specific tasks with an interactive editor, that accumulate in skills as you progress. The encouragement you get after completing a task is corny at first, but surprisingly addictive. Best of all, there's no chance of messing up your own website, so you can edit to your heart's content.
Firebug
A browser plugin called "Firebug" used to fill the role of being able to inspect an element years ago, but modern browsers (Chrome, Safari and Firefox) have incorporated this functionality right into the browser.
Ads & Ad Blockers
Ads are one way that bloggers can earn additional income, but seedy ad networks have ruined the public's trust with tracking, and obtrusive popups and autoplaying videos have ruined so many peoples experience that ad blockers are ubiquitous. Keep in mind that if you have embedded ads in your website, those spaces may simply appear as blank white spaces to people using adblockers.
Disabled Right Clicks
Some website owners have opted to use a plugin or javascript to disable right clicking in an attempt to prevent copy+pasting and saving images.
Don't disable right clicking.
All this does is irritate your visitors and make life more difficult for yourself. It does absolutely nothing to stop content theft.
Accept the fact that anything you put online can be copied and stolen.
This will stop the inspect functionality. As a best practice, we don't recommend attempting to disable right clicking as a preventative measure - it can be defeated in a number of ways including:
- automated web scrapers
- disabling javascript
- screenshots
- printing to PDF
- simply typing "view-source:" into the browser bar before a URL